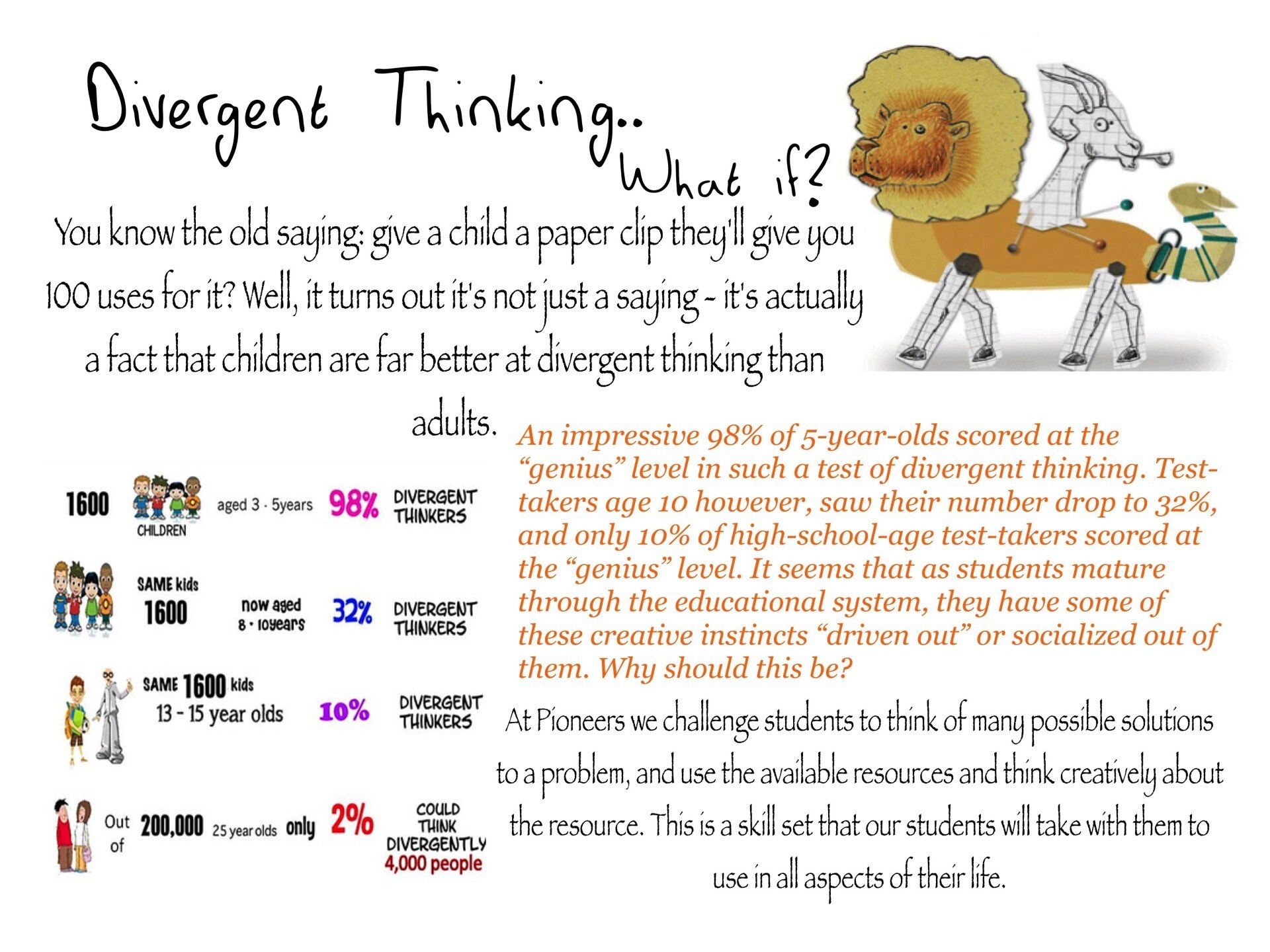
Fueling Success: The Impact of a Nutrient-Rich Diet on Behavior and Learning
In our fast-paced world, where academic and behavioural challenges often go hand in hand, one powerful solution may be on our plates. Emerging research suggests that the link between a nutrient-rich diet and improved behaviour and learning outcomes in children is more significant than we might have imagined.
As we strive to provide the best opportunities for our children's success, the role of nutrition in behaviour and learning cannot be overstated. A diet rich in diverse, nutrient-dense foods supports physical health and lays the foundation for enhanced cognitive function and positive behaviour. By understanding and implementing these nutritional strategies, parents and educators can contribute to a brighter, more focused future for the next generation.